LiveGood Magnesium: A Comprehensive Guide

Benefits, Importance, and Optimal Intake of LiveGood Magnesium
Magnesium is a basic mineral that is vital for many functions in the body. This is why LiveGood Magnesium could be so important. It is absolutely essential for maintaining health and performing tasks that are basic to being alive. And yet, this crucial mineral is not well-known, even among many health professionals. The mechanism by which it works is poorly understood, and its role in causing widespread deficiency is hardly talked about at all.
This blog post aims to remedy that slight by covering some of the basics of magnesium’s role in physiology, then moving on to discuss vitamin D as another essential nutrient that works synergistically with magnesium to maintain overall health. After discussing optimal intake levels for both nutrients, the advantages of LiveGood magnesium gluconate and glycinate, we’ll cover some of the most common causes of magnesium deficiency and the consequences of not enough magnesium in one’s diet.
The Importance of Magnesium
The human body can’t live without magnesium. It’s the fourth most abundant mineral in our bodies, and it’s vital for many physiological processes. There are over 300 enzymatic reactions in our bodies that don’t work properly—or at all—if they don’t have enough magnesium. That means that anything from simple tasks like closing your eyelids to more complex sequences of thought probably aren’t happening properly if you’re magnesium-deficient. Magnesium contributes to a broad range of functions, including:
- Energy Production: The production and storage of energy in our cells rely heavily on magnesium. This essential mineral is needed for the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), our main carrier of energy. It is also vital for keeping the floors of our power plants — the mitochondria — in good shape so they can convert the food we eat into energy that we can use.
- Protein Synthesis: Proteins are synthesized from amino acids in a process that involves magnesium. Muscle growth and repair, as well as overall cellular function, rely on this process. Without enough magnesium, the production of proteins is compromised.
- DNA and RNA Synthesis: The essential role of magnesium in DNA and RNA synthesis and repair makes it imperative for proper genetic function and cellular reproduction.
- Muscle and Nerve Function: The vital mineral magnesium has a direct effect on muscle and nerve function. It helps to maintain normal muscle duties and also helps to prevent cramps and spasms.
- Blood Glucose Control: Helping to keep blood sugar levels in check is one of the many important roles magnesium plays in our bodies. This essential mineral has been directly linked to insulin secretion and function, the two key processes involved in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Maintaining normal blood pressure is crucial for one’s health, and magnesium plays a key role in achieving this goal. This essential mineral has a direct effect on the relaxation of blood vessels, helping to keep them nice and loose so that blood can flow smoothly and easily through them.
The Benefits of LiveGood Magnesium
- Heart Health
- Maintaining a healthy heart rhythm is crucial, and magnesium plays a key role. It reduces hypertension and helps prevent cardiovascular disease. Magnesium helps keep blood vessels relaxed, lowering the risk of atherosclerosis and promoting overall heart health.
- Bone Health
- Bone formation is impossible without magnesium. Why? Because this essential mineral is needed to convert vitamin D into its active form, which in turn facilitates the absorption of calcium—a bone-building nutrient. And when it comes to keeping bones strong and dense, getting enough magnesium is a must. Several studies link higher intakes of this mineral with lower rates of osteoporosis.
- Mental Health
- The brain needs magnesium to function properly, and this mineral also plays a key role in mood regulation. It is sometimes called the “relaxation mineral” because it has a calming effect on the nervous system. Several studies have linked low levels of magnesium with an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders.
- Muscle Function
- For athletes and people with physically demanding lifestyles, magnesium is an essential mineral. It is necessary for muscle relaxation and contraction and helps prevent muscle cramps, spasms, and soreness. Many people do not get enough magnesium in their diets.
- Sleep Quality
- Sleep is more restorative when the body is adequately supplied with the necessary minerals. One of the most crucial of these minerals is magnesium, a mineral that is not only involved in regulating neurotransmitters and hormones related to sleep but also in muscle relaxation.
The Relationship between Vitamin D and Magnesium
The synergy between magnesium and vitamin D makes them work together better than either could alone. Magnesium is needed for the conversion of vitamin D into its active form, which helps keep calcium and phosphate levels in check. If you don’t get enough magnesium, your body can’t make enough active vitamin D, leaving you with insufficient levels of both minerals.
Benefits of Taking LiveGood Magnesium with LiveGood Vitamin D
- Improved Bone Health: Calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium are the three main nutrients needed for strong bones and reduced risk of fractures. While calcium and vitamin D usually take the spotlight, magnesium is just as important. It enhances calcium absorption and metabolism—thereby supercharging the formation of new bone.
- Enhanced Immune Function: The immune system can be greatly supported by magnesium and vitamin D. These two essential nutrients have been studied for their ability to enhance the function of the immune system, leading to reduced risk of infections and illnesses. Magnesium is involved in regulating the expression of genes important for the immune response, while vitamin D influences the differentiation and function of immune cells. Both nutrients also play a role in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, which are key factors in maintaining a healthy immune system. Additionally, vitamin D has been linked to tumor suppression and cancer prevention, further highlighting its importance for overall health. By ensuring adequate intake of both magnesium and vitamin D, individuals can take proactive steps towards supporting their immune function and resisting various health threats.
- Better Cardiovascular Health: Together, LiveGood magnesium and LiveGood vitamin D help keep blood pressure in check and improve overall cardiovascular function.
- Mood and Cognitive Function: This pair of nutrients can help improve mood and cognitive function. It can also help reduce the risk of depression and other mental health issues.
Optimal Magnesium Levels
The RDA (The recommended daily allowance) for magnesium varies by age, sex, and life stage:
- Adult Men (19-30 years): 400 mg/day
- Adult Men (31+ years): 420 mg/day
- Adult Women (19-30 years): 310 mg/day
- Adult Women (31+ years): 320 mg/day
- Pregnant Women: 350-400 mg/day
- Breastfeeding Women: 310-360 mg/day
It is very important to keep the right amount of magnesium in the body. A balanced diet can ensure sufficient magnesium intake for most people. However, some individuals may be at risk of deficiency and might need to take supplements to maintain optimal levels. These are people who have certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, or who are taking particular medications that can decrease magnesium levels. Additionally, older adults are more prone to magnesium deficiency because their ability to absorb it from food decreases with age. Depending on a person’s individual circumstances, a healthcare provider may recommend routine screening for low magnesium levels.


Causes of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency can result from variety of reasons, including:
- Poor Dietary Intake: Diets that are low in magnesium-rich foods can lead to deficiency.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Various conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and chronic diarrhea, can affect the body’s ability to absorb magnesium.
- Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can lead to increased magnesium excretion.
- Alcoholism: Excessive alcohol consumption/use can interfere with magnesium absorption and increase excretion.
- Medications: Medications like diuretics, proton pump inhibitors, and certain antibiotics can cause magnesium depletion.
Consequences of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency can cause some severe consequences on overall health, including and not limited to:
- Muscle Cramps and Spasms: Being low in magnesium can cause muscle cramps, twitches, and spasms.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Fatigue and weakness are well-known side effects of magnesium deficiency as it is crucial for energy production.
- Mental Health Issues: Having deficient levels of magnesium have been linked to increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders.
- Osteoporosis: Magnesium deficiency can impair bone health which can lead to osteoporosis and increased fracture risk.
- Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease: Magnesium is vital for maintaining healthy blood pressure, and evidence suggests that its deficiency may lead to hypertension and even cardiovascular diseases.
Benefits of LiveGood Magnesium Gluconate
Magnesium gluconate is a highly bio-available form of magnesium which makes it a good choice when looking for a quality supplement. It offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Absorption: LiveGood Magnesium gluconate is well-absorbed by the body which ensures it as an effective supplement.
- Digestive Health: This form of LiveGood magnesium is gentle on the stomach and less likely to cause digestive discomfort compared to other forms.
- Muscle Function: Magnesium gluconate helps prevent and alleviate muscle cramps and spasms.
- Cardiovascular Health: It also helps maintain normal blood pressure levels and supports heart health.
Benefits of LiveGood Magnesium Glycinate
Magnesium glycinate is another highly bio-available form of magnesium. It is known for its calming effects and having minimal side effects. Its benefits include:
- Improved Sleep: Magnesium glycinate can help promote relaxation and improves sleep quality.
- Reduced Anxiety: This form of magnesium has a calming effect on the nervous system which can help reduce anxiety and stress.
- Enhanced Absorption: Magnesium glycinate is easily absorbed and less likely to cause digestive issues. So if you already have a sensitive stomach, LiveGood magnesium glycinate is a great choice.
- Muscle Relaxation: It also helps relax muscles and prevent cramps which makes it beneficial for athletes and individuals with physically demanding lifestyles.
Best Food Sources of Magnesium
Having a balanced diet rich in magnesium can help maintain optimal levels of magnesium. Some of the best food sources of magnesium include:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are excellent sources of magnesium.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds are magnesium-rich.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat products provide substantial amounts of magnesium.
- Legumes: Black beans, chickpeas, lentils, and kidney beans are good sources of magnesium.
- Fish: Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel contain magnesium.
- Avocado: This nutrient-dense fruit is a good source of magnesium.
- Dark Chocolate: High-quality dark chocolate is a delicious source of magnesium.
- Bananas: Bananas offer a moderate amount of magnesium along with other essential nutrients.
- And of course if you are not getting all the magnesium you need then LiveGood magnesium is a great choice as a supplement. Containing both magnesium glycinate and magnesium gluconate makes this supplement a premium choice.
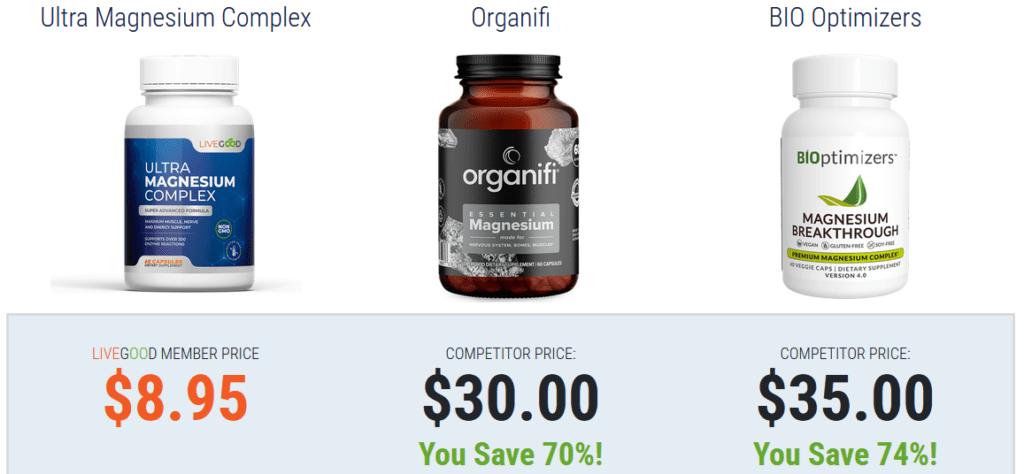
Who Should Avoid Taking LiveGood Magnesium Supplements
Yes, taking a LiveGood magnesium supplement is beneficial for many people but certain individuals should avoid them or consult a healthcare professional before starting supplementation:
- Individuals with Kidney Disease: Impaired kidney function can lead to an accumulation of magnesium which can cause toxicity.
- People on Certain Medications: Magnesium supplements can interact with certain medications such as antibiotics, diuretics, and proton pump inhibitors. You should consult a healthcare provider if you are on these medications and also do your do diligence on handy dandy Google. There are so many clinical studies and information out there that it is literally impossible for any doctor to know all of the current and past information available. In the future, Doctor AI will change the way a patient is diagnosed forever.
- Those with Heart Block: High doses of magnesium can exacerbate heart block. Heart block is a condition where the heart’s electrical signals are impaired.
- Individuals with Myasthenia Gravis: This particular autoimmune neuromuscular disorder can be worsened by magnesium supplementation.
Magnesium Conclusion
An essential mineral, magnesium plays a huge part in maintaining the body’s health. It is involved in energy production, making sure muscles and nerves function properly, and even in achieving a healthy bone density. Several studies have linked magnesium with heart health. They have shown that this crucial mineral can help prevent hypertension (high blood pressure) and aid in keeping coronary arteries unstopped—minus the hazards of plaque buildup. Magnesium also has a hand in preventing arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat). Because the body cannot make enough of this essential nutrient, one must consume it through food or supplements to stay optimally healthy.
Incorporate magnesium-rich foods into your diet and consider the synergistic benefits of taking magnesium with vitamin D. Supplement with LiveGood Ultra Magnesium Complex if needed. Always consult a healthcare professional if you have any underlying health conditions or are on medications that may interact with magnesium.
If you support your magnesium intake, you can support your body’s vital functions and enjoy a healthier and more balanced life.
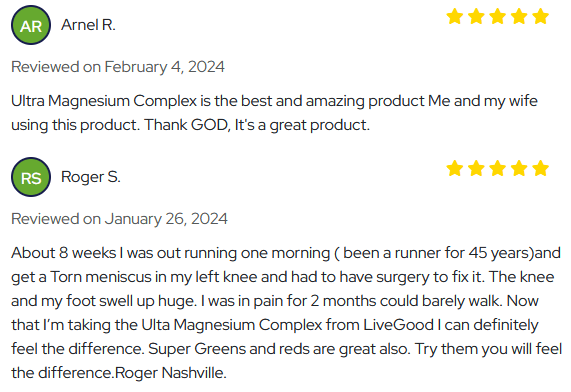
LiveGood Ultra Magnesium Complex Reviews



Sources:
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) Office of Dietary Supplements – Magnesium: NIH ODS Magnesium
- Mount Sinai – Magnesium
- American Journal of Clinical Nutrition – Magnesium and Vitamin D
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health – The Nutrition Source: Harvard
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs): NIH RDAs
- Journal of the American College of Nutrition – Magnesium deficiency: JACN
- Differences between magnesium gluconate and glycinate
- National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Magnesium Fact Sheet for Health Professionals: NIH Supplements
- Food Data Central – Magnesium content in foods
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health – Magnesium: Harvard Magnesium
- Mayo Clinic – Magnesium supplements: Mayo Clinic
- Linus Pauling Institute – Micronutrient Information Center: Linus Pauling Institute
- Cleveland Clinic – Magnesium: Cleveland Clinic
These sources provide detailed information on the various aspects of magnesium, its benefits, dietary sources, and the importance of maintaining optimal levels. They are from reputable institutions and peer-reviewed journals, ensuring the reliability of the information.





One Comment